What is a Burette? Definition, Uses, Parts and Diagram Explained.
Precision is very important in any chemistry laboratory area- an element that a burette cannot be ignored.
A burette is a long and graduated tube made of glass with a stopcock at the bottom able to precisely measure and dispense liquids in drops.
A burette has been used already in case you ever did a titration experiment. This blog explain what a burette is, its uses, its parts, a diagrammatic illustration and the difference between a burette and a pipette.
What does this instrument mean in Chemistry?
A burette is a lab glassware that is utilized in measuring specific volumes of a liquid reagent during analytical experiments. It is usually used to determine the concentration of an unknown solution through titration- a controlled reaction between two liquids than the ones that are used.
Millilitre graduations (mL) are given on burettes, and have a precision of 0.1 mL, meaning that they are important in experiments where very specific volumes are required.
Concisely, a burette allows the accurate measurement of the volume of a liquid to carry out the analysis of chemicals accurately.
Practical uses of this instrument?
Quantitative analysis (and especially titration) involves adding one liquid to another until the reaction is complete (the endpoint), with the use of a burette.
Its application is defined in different spheres:
- In Chemistry Laboratories: to titrate and to measure the volumes of the solutions.
- In Pharmacy: to prepare or standardize the drug preparations in the form of liquids.
- Nursing and Biology: to ensure controlled liquid transfers during laboratory tests.
- Science and Education: to illustrate the action of chemical reactions and perform experiments of a practical character.
- In titration, the titrant is added drop-by-drop through the use of a burette until an indicator is used to signal a neutralisation point.
- Therefore, the following question is: what is a burette used in the course of titration? the answer is the following: to produce the accurate volumes of liquid in the course of a reaction.
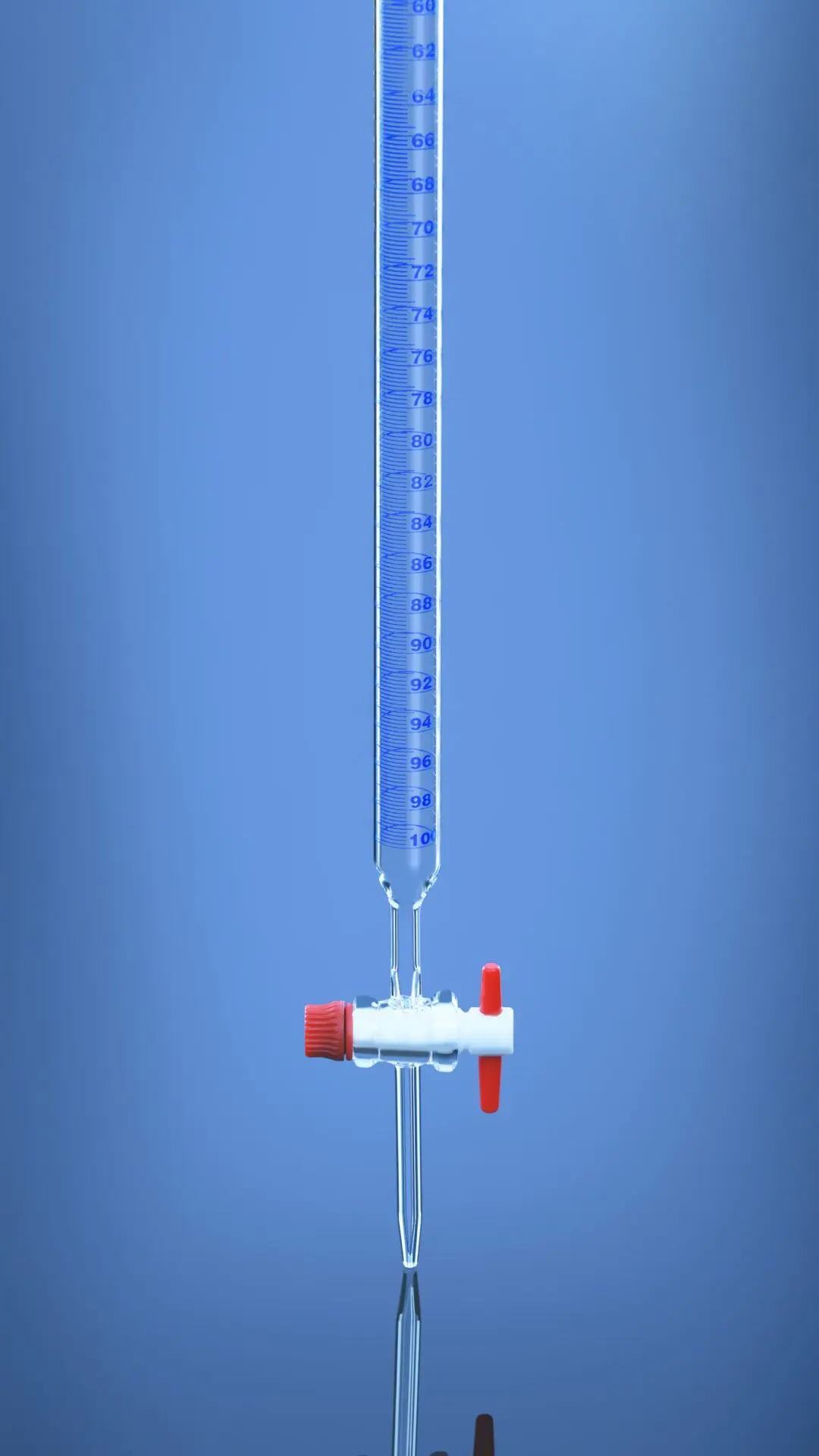


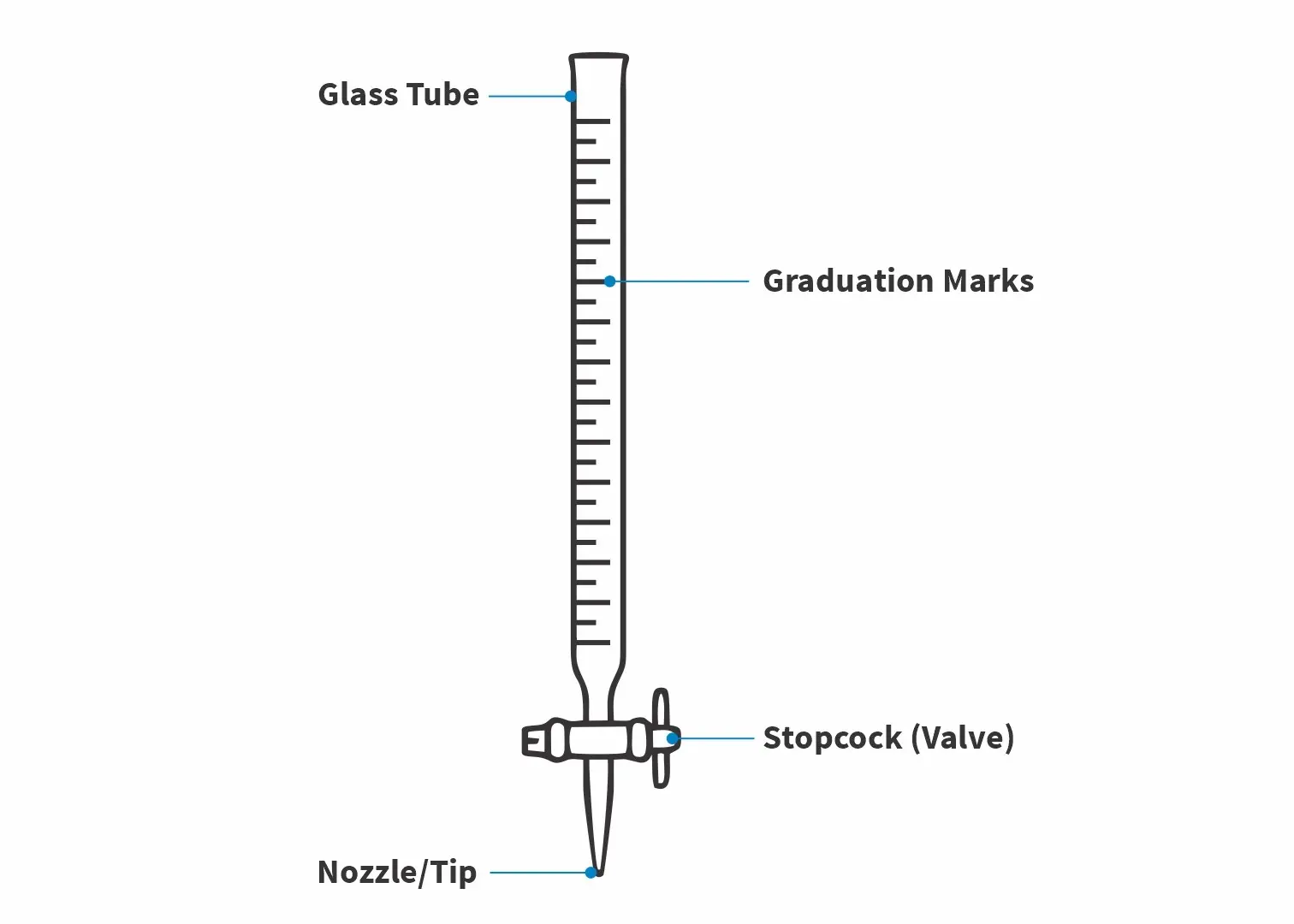

Main Components of this Instrument (including Diagram)
- Glass tube: This is the long, transparent structure that is usually of borosilicate glass, but has the volume graduations.
- Stopcock (valve): This is found at the bottom, which controls the drops of liquid flowing.
- Nozzle / tip: Discharges the liquid into the flask as it is titrated.
- Graduation marks An indicator of the precise liquid volume.
A burette is usually held on a burette stand with a burette clamp to ensure the burette is straight and at rest throughout experiments.
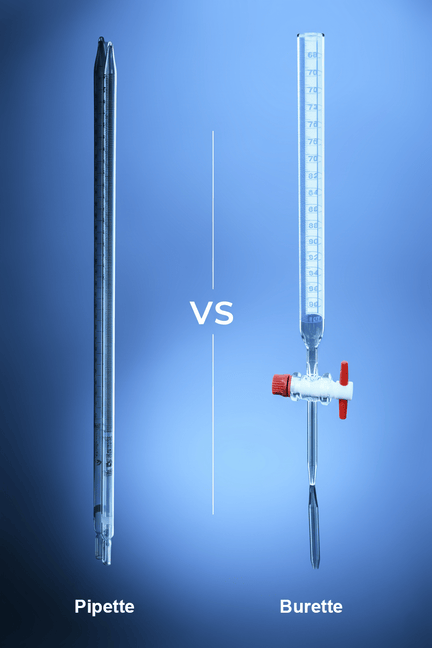
Burette vs. Pipette What is the difference?
Both pipettes and are used in the correct measurement of liquid but the functions are different:
| Pipette | Burettes | |
|---|---|---|
| Function | Transfers fixed volume. | Dispenses variable volume |
| Accuracy | Up to 0.01 ml | Up to 0.1 ml |
| Flow control | Manual suction | Valve-controlled flow |
| Application | Solution transfer | Titration experiments |
A dispensing and a transferring process is then followed and therefore a burette and a pipette are used respectively. They are both used in combination in most titration systems.

Summary: A general purpose of a Burette.
There are five main purposes of a burette to which we shall make a short summing up:
- It is used in titration in order to measure and dispense solutions with precision.
- Applied in the pharmacy to make the right chemical mixtures.
- Applied in laboratories both in the testing of reactions and in research.
- Applied in quality tests and analysis experiments.
- Applied in schools and colleges to do demonstrations.
So, when someone questions what a burette is, it is possible to reply-
Measurement and dispensing of accurate volume of liquids in chemical analysis is done by means of burette.
Frequently Asked questions about Burettes.
In its formulation and analysis, a burette in pharmacy helps in accurate preparation and dilution of drug solutions.
To maintain the accuracy of the titration, a burette stand is used to hold the burette on its own while standing upright.
Burettes are used in a laboratory of nursing and biology to measure fluids, in research experiments, and the preparation of solutions.
The burette is firmly attached to a stand by a burette clamp to ensure that it does not spill or give inaccurate measurements.